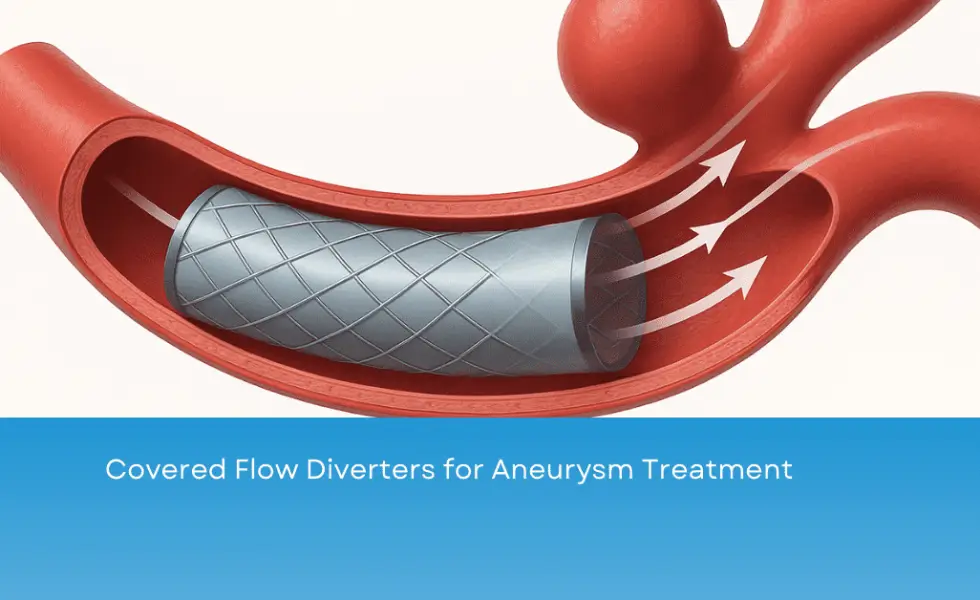
Covered Flow Diverters for Aneurysm Treatment: A Breakthrough in Endovascular Therapy
Covered flow diverters for aneurysm treatment are advanced endovascular devices that improve patient outcomes by accelerating vessel healing, reducing complications, and shortening recovery time. This article explores how these devices use specialized covering technologies—including polymeric, bioactive, and drug-eluting layers—to enhance the treatment of intracranial aneurysms and other vascular disorders.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand why covered flow diverters are becoming a cornerstone in modern aneurysm management.
What Are Covered Flow Diverters?
Covered flow diverters for aneurysm treatment are stent-like devices inserted into blood vessels to redirect blood flow away from aneurysms. They are commonly used for:
Intracranial aneurysms (especially large or wide-necked)
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
Carotid-cavernous fistulas (CCFs)
Unlike traditional coiling techniques, covered flow diverters focus on long-term vessel remodeling, making them highly effective for complex aneurysm treatment. Learn more about endovascular devices and procedures.
Benefits of Covered Flow Diverters for Aneurysm Treatment
Adding coverings to flow diverters provides several advantages:
Accelerated endothelialization – faster regrowth of the vessel lining
Improved biocompatibility – reduced inflammation and clotting risks
Higher aneurysm occlusion rates – better long-term closure
Shorter patient recovery – fewer complications and quicker stabilization
Reduced hospital stays – lower healthcare costs
For additional clinical insights, see this review on aneurysm treatment outcomes (outbound link).
Covering Technologies in Flow Diverters
Different coatings enhance the performance of covered flow diverters for aneurysm treatment:
Polymeric Coatings
Polyurethane, polycarbonate urethane (ChronoFlex®), and fluoropolymers provide controlled porosity and smooth surfaces to support faster vessel healing.
Bioactive Coatings
Incorporating extracellular matrix proteins, adhesion peptides, or growth factors stimulates natural tissue regeneration.
Drug-Eluting Coatings
Controlled release of agents like sirolimus or heparin prevents thrombosis and promotes endothelialization.
Hybrid Approaches
Combining polymeric, bioactive, and drug-eluting strategies maximizes device performance.
Challenges of Covered Flow Diverters for Aneurysm Treatment
Despite their promise, covered flow diverters for aneurysm treatment face challenges:
Maintaining flexibility and deliverability despite additional layers
Ensuring long-term durability without delamination or degradation
Meeting regulatory and clinical validation requirements
Ongoing research in biomaterials and coatings is helping to overcome these limitations. For more information, see our vascular device research page.
Conclusion: The Future of Aneurysm Treatment
Covered flow diverters for aneurysm treatment represent a breakthrough in endovascular therapy. By reducing the time to full therapeutic effect, these devices improve patient outcomes, shorten recovery time, and decrease hospital stays. As innovations in covering technologies continue, these devices are poised to become a cornerstone in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms and complex vascular pathologies.
👉 Stay updated on advanced covering technologies and the latest in vascular device innovation by following our blog.